Forms
anuragG37202438741 total contribution
Published Aug 4, 2021Updated Sep 15, 2023
Contribute to Docs
In HTML, forms are used for gathering and sending user input to an external source (like a server) for processing. This is done with the <form> element, which contains various labels and inputs.
Syntax
<form><!-- Form elements --></form>
Example
The following is an example of an HTML form that features <input> elements:
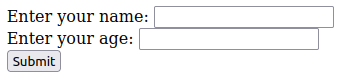
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head> </head><body><form method="post" action="http://server1">Enter your name:<input type="text" name="fname" /><br />Enter your age:<input type="text" name="age" /><br /><input type="submit" value="Submit" /></form></body></html>
The renderd output of above looks like this:
Video Walkthrough
Watch this video for a step-by-step tutorial on creating HTML forms.
All contributors
- anuragG37202438741 total contribution
 CaupolicanDiaz142 total contributions
CaupolicanDiaz142 total contributions sczerman14 total contributions
sczerman14 total contributions cheriii1 total contribution
cheriii1 total contribution BrandonDusch580 total contributions
BrandonDusch580 total contributions christian.dinh2476 total contributions
christian.dinh2476 total contributions- Anonymous contributorAnonymous contributor3071 total contributions
- anuragG3720243874
- CaupolicanDiaz
- sczerman
- cheriii
- BrandonDusch
- christian.dinh
- Anonymous contributor
Looking to contribute?
- Learn more about how to get involved.
- Edit this page on GitHub to fix an error or make an improvement.
- Submit feedback to let us know how we can improve Docs.

